Building an index¶
Nixiesearch index is just a regular index like in Elastic/OpenSearch/SOLR, but with the following differences:
- Indexes are created by defining their schemas in a config file. It is deliberately not possible to create an index at runtime using REST API, as Nixiesearch instances have an immutable configuration.
- Index always has a strict schema defined. Schemaless approach is user-friendly, but you will eventually have 10 different ways to store a boolean field, like it usually happens in MongoDB 🫠.
To add a set of documents to an index, you need to perform these two steps:
- define an index mapping in a config file. Nixiesearch is a strongly-typed document storage system, so dynamic mapping is not supported.
- write documents to the index, either with push-based REST API or with pull-based stream ingestion.
Note
Dynamic mapping in most search engines is considered an anti-pattern: the engine cannot correctly guess how are you going to query documents, so by default all fields are marked as searchable, facetable, filterable and suggestable. This results in slow ingestion throughput and huge index size.
Index mapping¶
To define an index mapping, you need to add an index-specific block to the schema section of the configuration file. You can also configure indexing performance settings like merge policies in the configuration:
schema:
my-first-index:
fields:
title:
type: text
search:
lexical:
analyze: english
price:
type: float
filter: true
In the example above we defined an index my-first-index with two fields title and price. Index is stored on disk by default.
Each field definition in a static mapping has two groups of settings:
- Field type specific parameters - like how it's going to be searched for text fields. In the example above we only allowed
lexicalsearch over thetitlefield. See the mapping reference for text fields to see how to enable semantic and hybrid search. - Global parameters - is this field can be stored, filtered, faceted and sorted.
Go to the mapping reference section for more details on all field parameters.
Writing documents to an index¶
Internally Nixiesearch implements a pull-based indexing - the service itself asks for a next chunk of documents from an upstream source. See File-based indexing and Stream indexing from Apache Kafka for more examples on this approach.
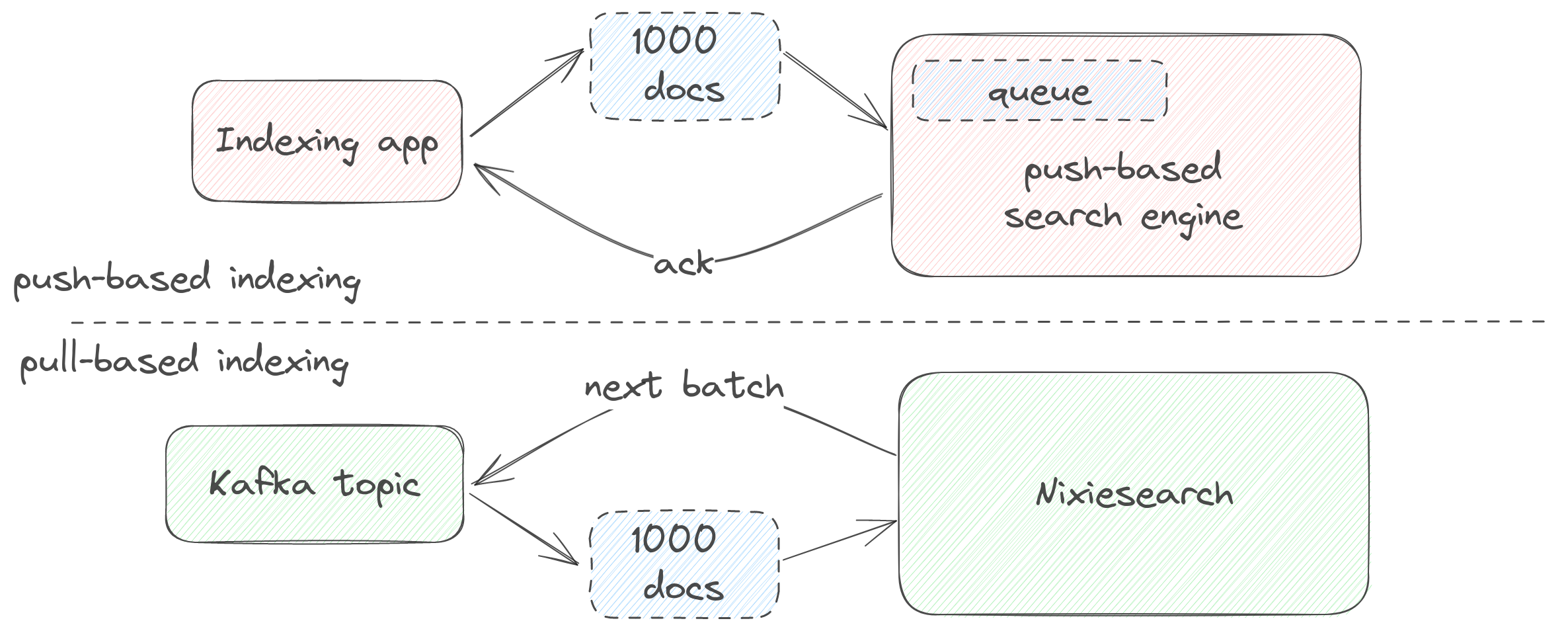
For convenience, Nixiesearch can emulate a push-based approach via REST API you probably got used with other search engines - your app should submit a JSON payload with documents and wait for an acknowledgement.
Starting Nixiesearch¶
Nixiesearch has multiple ways of running indexing:
- Offline indexing. Useful when performing full reindexing from static document source, like from a set of files, or from Kafka topic.
- Online indexing. For folks who got used to Elasticsearch with REST API.
For the sake of simplicity we can start Nixiesearch in a standalone mode, which bundles both searcher and indexer in a single process with a shared REST API.
docker run -it -p 8080:8080 -v .:/data nixiesearch/nixiesearch:latest standalone --config /path/to/conf.yml
Note
Standalone mode is intended for small-scale local deployments and developer environments, not for a production use. If you plan to use Nixiesearch with real customer traffic, consider using a distributed deployment with S3-based storage.
Indexing REST API¶
Each Nixiesearch index has an /v1/index/<index-name> REST endpoint where you can HTTP POST your documents to.
This endpoint expects a JSON payload in one of the following formats:
- JSON object: just a single document.
- JSON array of objects: a batch of documents.
- JSON-Line array of objects: also a batch of documents, but simpler wire format.
For example, writing a single document to an dev index can be done with a cURL command:
curl -XPOST -d '{"title": "hello", "color": ["red"], "meta": {"sku":"a123"}}'\
http://localhost:8080//v1/index/my_dev_index
Note
To have proper back-pressure mechanism, prefer using a pull-based indexing with Apache Kafka or with offline file-based ingestion.
Streaming document indexing¶
With pull-based streaming indexing supported natively, it becomes trivial to implement these typical scenarios:
- Batch full re-indexing: take all documents from a datasource and periodically re-build index from scratch.
- Distributed journal as a single source of truth: use Kafka compacted topics as a view over last versions of documents, with real-time updates.
- Large dataset import: import a complete set of documents from local/S3 files, maintaining optimal throughput and batching.
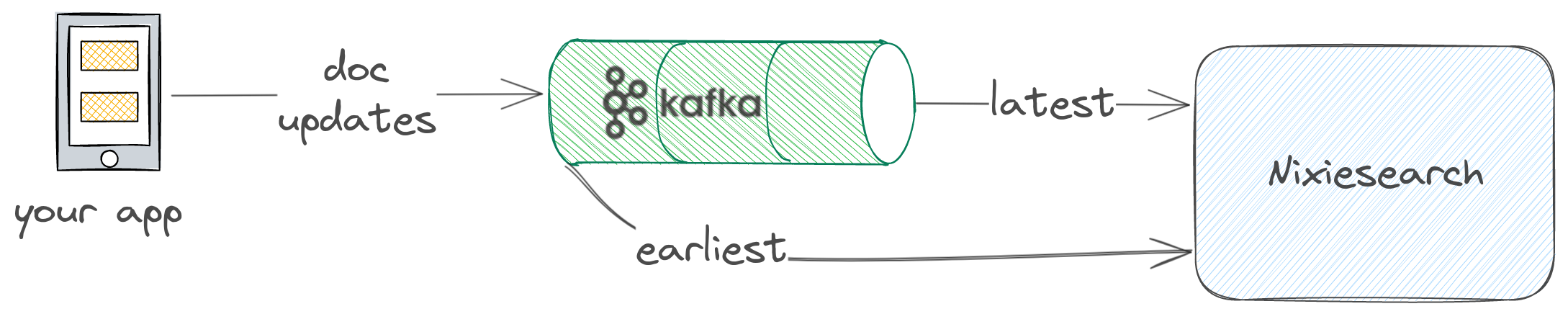
Nixiesearch supports Apache Kafka, AWS S3 (and also compatible object stores) and local files as a source of documents for indexing.
If you have your dataset in a JSON file, instead of making HTTP PUT with very large payload using REST API, you can invoke a nixiesearch index sub-command to perform streaming indexing in a separate process:
docker run -itv .:/data nixiesearch/nixiesearch:latest index file \
--config /data/conf.yml --index <index name> \
--url file:///data/docs.json
Where <your-local-dir> is a directory containing the conf.yml config file and a docs.json with documents for indexing.
See index CLI reference and Supported URL formats for more details.
Next steps¶
In the next section, learn how you can create an index mapping.